CANNABINOIDS
Cannabinoids, like THC, CBD and CBG, are organic chemical compounds that, with terpenes, make up the building blocks of the cannabis plant. Translating into medicinally valuable relief, cannabinoids have been successfully used in the treatment of conditions such as cancer, seizures, and Parkinson’s disease and symptoms such as inflammation, pain and nausea.
Cannabis cannabinoids provide such medical efficacy to humans because they mimic our own naturally produced endocannabinoids, and bind to the same receptors, located throughout the brain and body. The human endocannabinoid system is responsible for regulating many different body systems, including pain, memory, mood and appetite. The unique ability of cannabis cannabinoids to be able to communicate with the human body in the same manner that it communicates with itself makes it an ideal medicine for humans.
The following sections provide additional information on some of the more well-known and widely referenced cannabinoids – we’ll help explain what these cannabinoids do and how they may affect the body. We hope that you find this information helpful.
JUMP TO
CBG
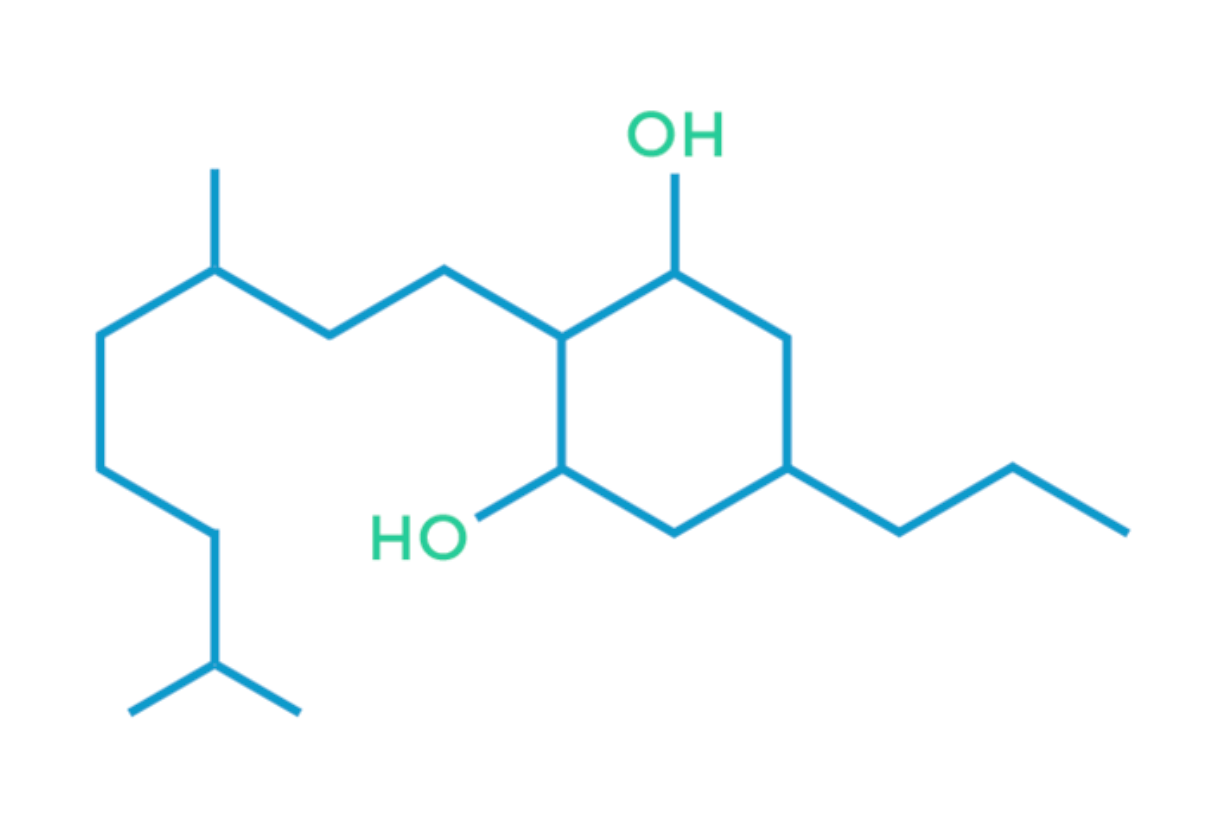
Cannabigerol, or CBG, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid typically most abundant in low-THC and high-CBD cannabis strains, including hemp. Like THC, CBG reacts with the cannabinoid receptors in the brain. CBG, however, acts as a buffer to the psychoactivity of THC by working to alleviate the paranoia sometimes caused by higher levels of THC.
CBG works to fight inflammation, pain, nausea and works to slow the proliferation of cancer cells. Research has shown it also significantly reduces intraocular eye pressure caused by glaucoma. Strains high in CBG will be beneficial treating conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s disease, and cancer.
Cannabinoids bind to receptor sites in the brain and body – this system of receptors is referred to as the Endocannabinoid System.
Effects and Benefits
Research has shown that CBG is effective in the treatment of a variety of symptoms and conditions. Examples of conditions for which CBG is particularly effective in providing symptom relief are listed below:
- Glaucoma
- Cancer
- Crohn’s disease
- Irritable bowel syndrome
LINKS TO RESEARCH
- Colon carcinogenesis is inhibited by the TRPM8 antagonist cannabigerol, a Cannabis-derived non-psychotropic cannabinoid.
READ STUDY →
- A cannabigerol quinone alleviates neuroinflammation in a chronic model of multiple sclerosis.
READ STUDY →
- A cannabigerol derivative suppresses immune responses and protects mice from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
READ STUDY →
- Beneficial effect of the non-psychotropic plant cannabinoid cannabigerol on experimental inflammatory bowel disease.
READ STUDY →
THCV
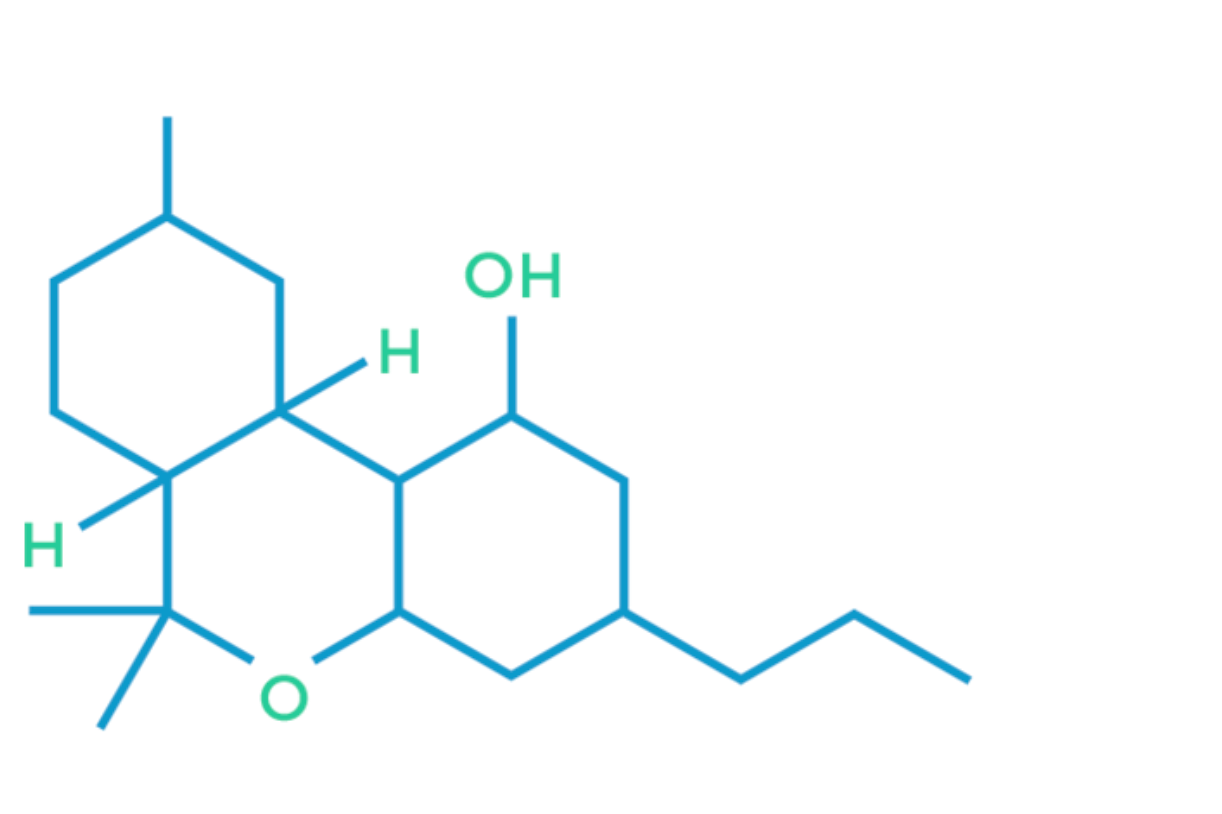
Tetrahydrocannabivarin, or THCV, is a psychoactive cannabinoid found most prevalently in Sativa strains of cannabis. It is known to produce a more motivated, alert and energizing feeling of euphoria. For this reason, it is often recommended for daytime or any time when functionality is important.
THCV relieves stress and research shows it can help to reduce or even prevent anxiety and panic attacks. For this reason, it plays an important role in the treatment of post-traumatic-stress-disorder (PTSD). It is also neuroprotective, so it is ideal for treating conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. Unlike THC, THCV works to suppress the appetite so it is not recommended for patients suffering from cachexia or anorexia nervosa.
Effects and Benefits
Research has shown that THCV is effective in the treatment of a variety of symptoms and conditions. Examples of conditions for which THCV is particularly effective in providing symptom relief are listed below:
- PTSD
- Parkinson’s disease
- Seizures (including epilepsy)
- Alzheimer’s disease
LINKS TO RESEARCH
- Symptom-relieving and neuroprotective effects of the phytocannabinoid Δ9-THCV in animal models of Parkinson’s disease.
READ STUDY →
- The plant cannabinoid Δ9‐tetrahydrocannabivarin can decrease signs of inflammation and inflammatory pain in mice.
READ STUDY →
THCA
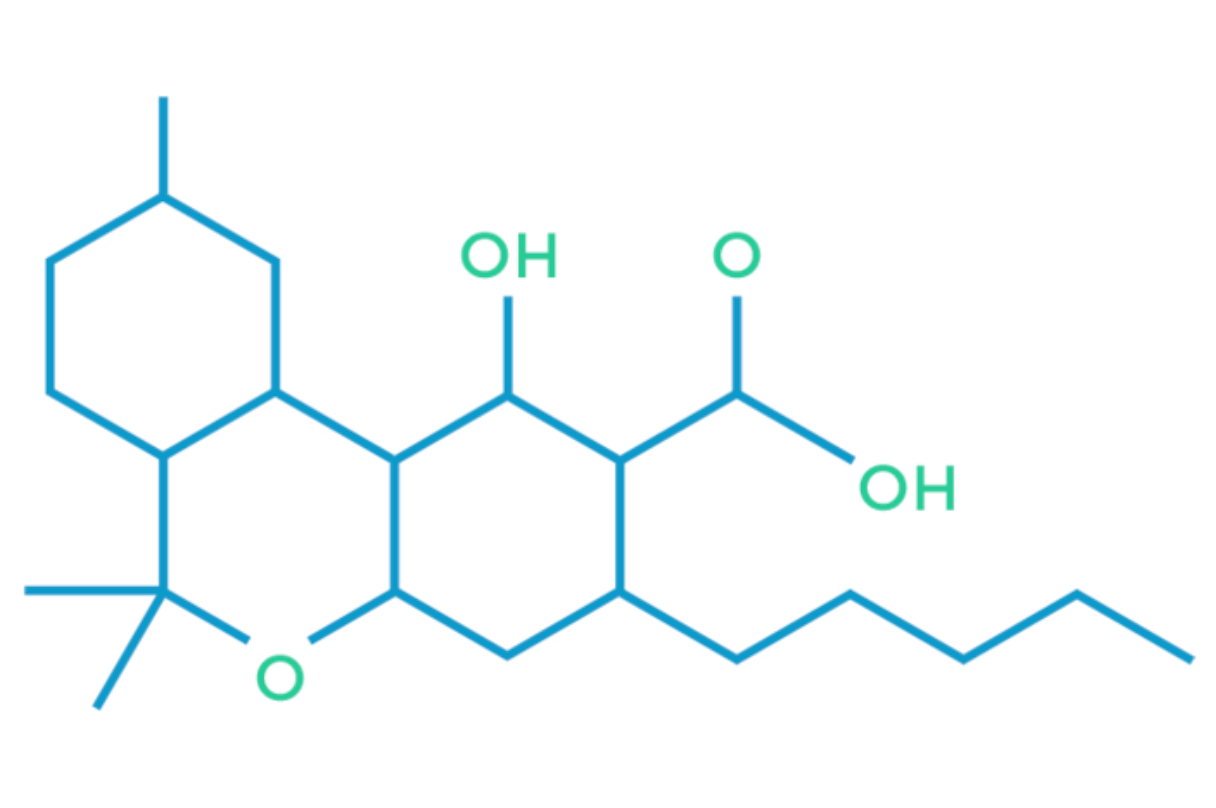
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is the most abundant non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis. The health benefits provided by THCA are most well absorbed by the body through a raw method of consumption such as cannabis juicing. THCA works to relieve inflammation, pain and is an ideal cannabinoid for treating symptoms of such conditions as arthritis, seizures.
THCA is an effective neuroprotectant, so it is beneficial in the treatment of such conditions as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. It can also help to stimulate the appetite in patients suffering from cachexia and anorexia nervosa. Most impressively, research shows that THC-A helps to slow the proliferation of cancerous cells.
Effects and Benefits
THCA is an effective neuroprotectant, so it is beneficial in the treatment of such conditions as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. It can also help to stimulate the appetite in patients suffering from cachexia and anorexia nervosa. Most impressively, research shows that THC-A helps to slow the proliferation of cancerous cells.
Research has shown that THCA is effective in the treatment of a variety of symptoms and conditions. Examples of conditions for which THCA is particularly effective in providing symptom relief are listed below:
- Cancer
- Seizures (including epilepsy)
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Cachexia
LINKS TO RESEARCH
- Non-THC cannabinoids inhibit prostate carcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo: pro-apoptotic effects and underlying mechanisms.
READ STUDY →
- Cannabinoids for Medical Use: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
READ STUDY →
- Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid reduces nausea-induced conditioned gaping in rats and vomiting in Suncus murinus.
READ STUDY →
CBN
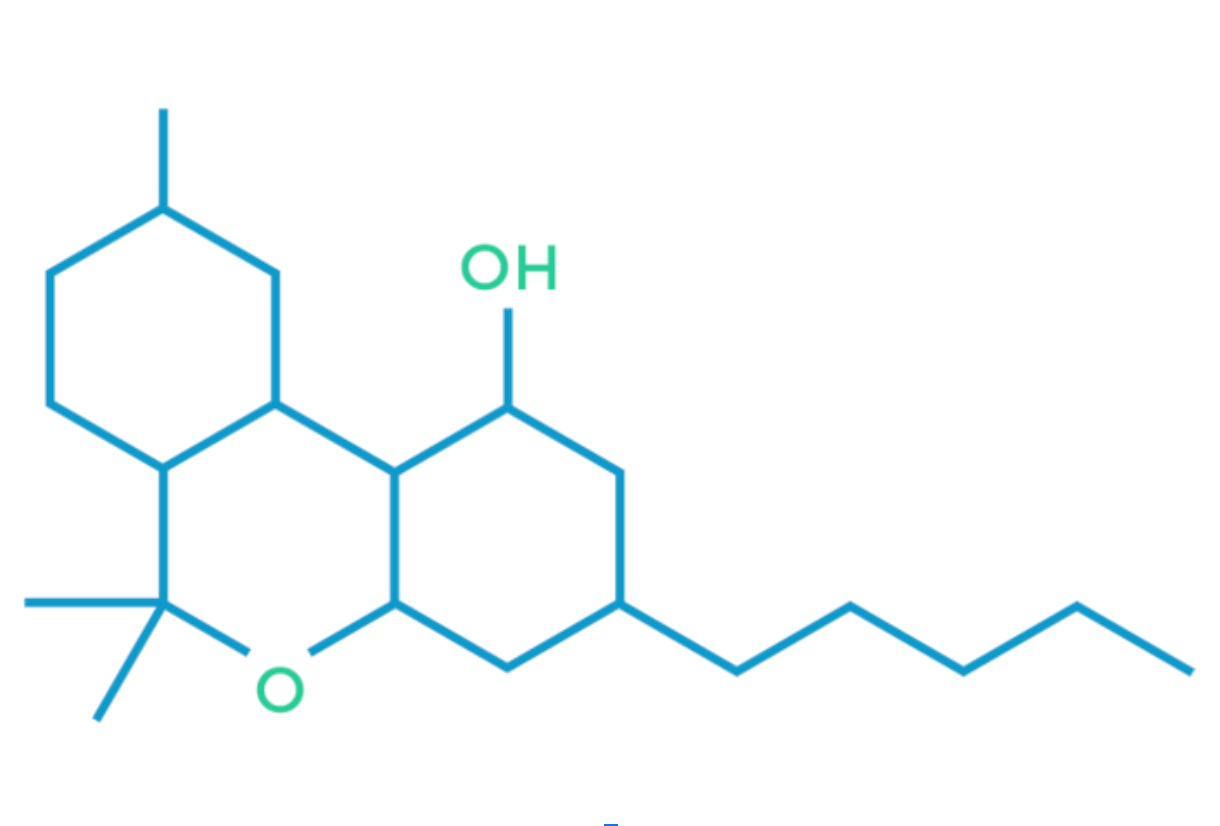
Cannabinol, or CBN, is a mildly psychoactive component found in cannabis which, like strongly psychoactive THC, is derived from tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THC-A). CBN is created when THC-A oxidizes.
CBN can be used effectively as a sleep aid or sedative. This cannabinoid has also been shown to help regulate the immune system and works to relieve the pain and inflammation caused by several conditions, including arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Studies show that it can be used to reduce the intraocular eye pressure caused by glaucoma. CBN acts as an anticonvulsant, so it is also beneficial to patients suffering from seizure disorders including epilepsy.
Effects and Benefits
Research has shown that CBN is effective in the treatment of a variety of symptoms and conditions. Examples of conditions for which CBN is particularly effective in providing symptom relief are listed below:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Seizures (including epilepsy)
- Crohn’s disease
- Chronic post-operative pain
LINKS TO RESEARCH
- Antibacterial cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa: a structure-activity study.
READ STUDY →
- Turning Over a New Leaf: Cannabinoid and Endocannabinoid Modulation of Immune Function.
READ STUDY →
- Pharmacologic interaction between cannabinol and delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol.
READ STUDY →
THC
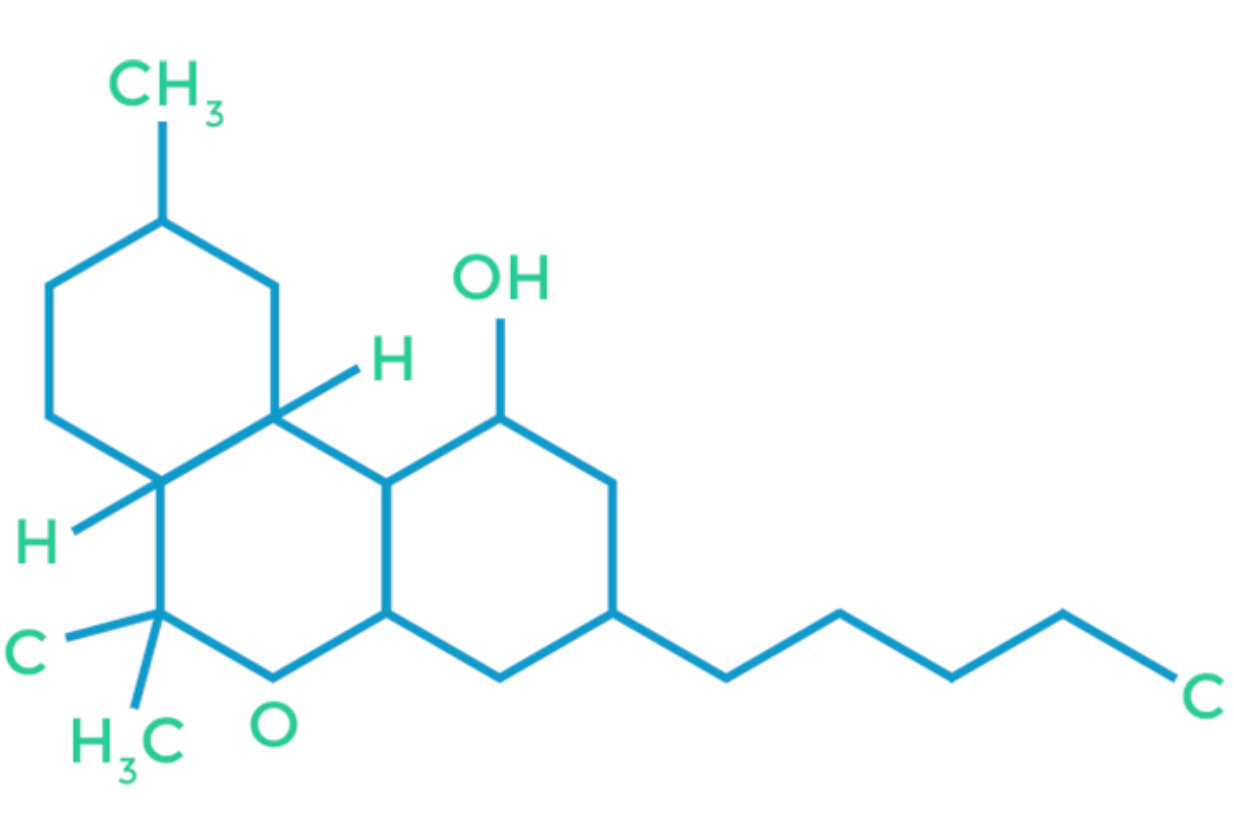
Tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, is the most well-known and most often the most prevalent cannabinoid found in cannabis. This is the psychoactive component known to produce euphoria, which is more often described as the feeling of being “high.”
THC binds primarily to the receptors found throughout the brain. Research has shown THC to work to reduce or even eliminate pain, nausea, and stress while also helping to stimulate the appetite and combat insomnia. In high doses, THC may cause some patients to feel paranoia or an increased heart rate, but these adverse effects will subside with time.
Effects and Benefits
Research has shown that THC is effective in the treatment of a variety of symptoms and conditions. Examples of conditions for which THC is particularly effective in providing symptom relief are listed below:
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Cancer
- Chronic postoperative pain
- Fibromyalgia
LINKS TO RESEARCH
- Cannabidiol Enhances the Inhibitory Effects of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol on Human Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation and Survival.
READ STUDY →
- The effectiveness of cannabinoids in the management of chronic nonmalignant neuropathic pain: a systematic review.
READ STUDY →
- Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol alone and combined with cannabidiol mitigate fear memory through reconsolidation disruption.
READ STUDY →
- Tetrahydrocannabinol for treatment of chronic pain.
READ STUDY →
CBDV
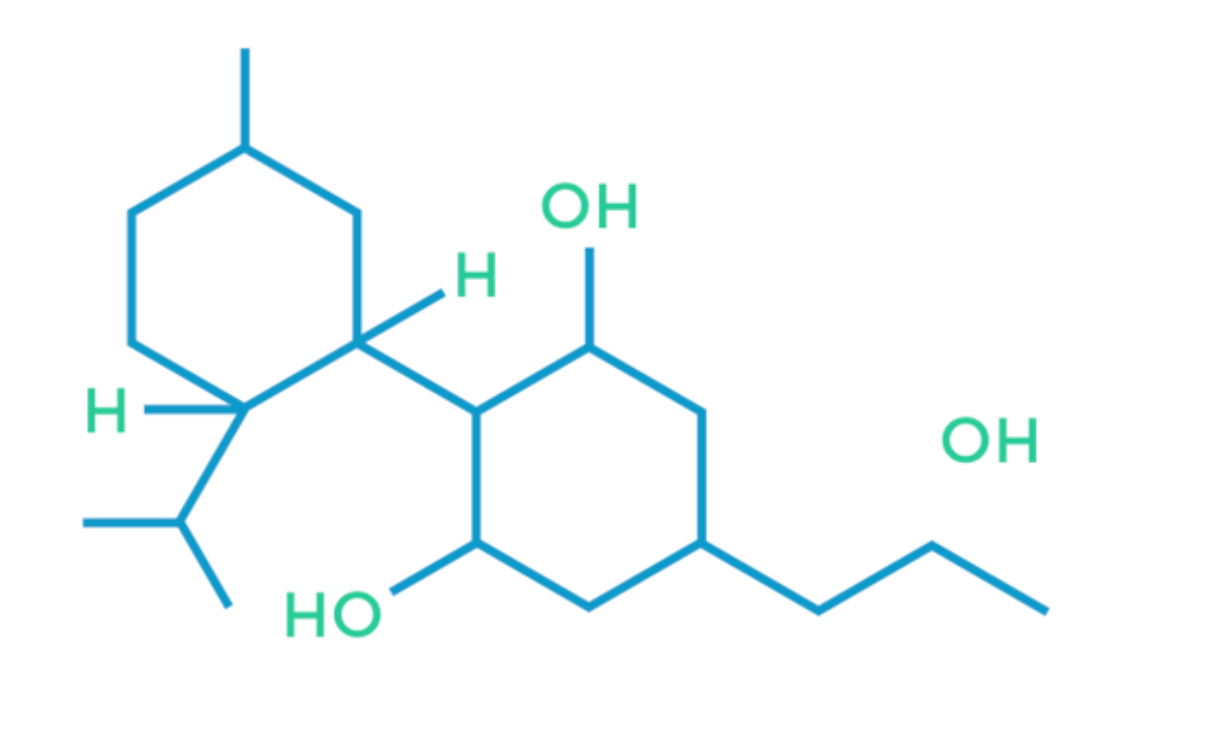
Cannabidivarin (CBDV) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that will not cause the euphoric feeling of being “high.” It is found more prevalently in indica strains, specifically landrace indica strains, and strains that are lower in tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
Like CBD, CBDV significantly reduces the frequency and severity of seizures. It also reduces or even eliminates nausea associated with several conditions, and helps to reduce inflammation throughout the body. CBDV is also beneficial in the treatment of pain and mood disorders.
Effects and Benefits
Research has shown that CBDV is effective in the treatment of a variety of symptoms and conditions. Examples of conditions for which CBDV is particularly effective in providing symptom relief are listed below:
- Seizures
- Crohn’s
- HIV/AIDS
- Multiple Sclerosis
LINKS TO RESEARCH
- Cannabinoid actions at TRPV channels: effects on TRPV3 and TRPV4 and their potential relevance to gastrointestinal inflammation.
READ STUDY →
- Cannabidivarin is an anticonvulsant in mice and rats.
READ STUDY →
- Cannabidivarin (CBDV) suppresses pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced increases in epilepsy-related gene expression.
READ STUDY →
- Evaluation of the potential of the phytocannabinoids, cannabidivarin (CBDV) and Δ(9) -tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), to produce CB1 receptor inverse agonism symptoms of nausea in rats.
READ STUDY →
CBD
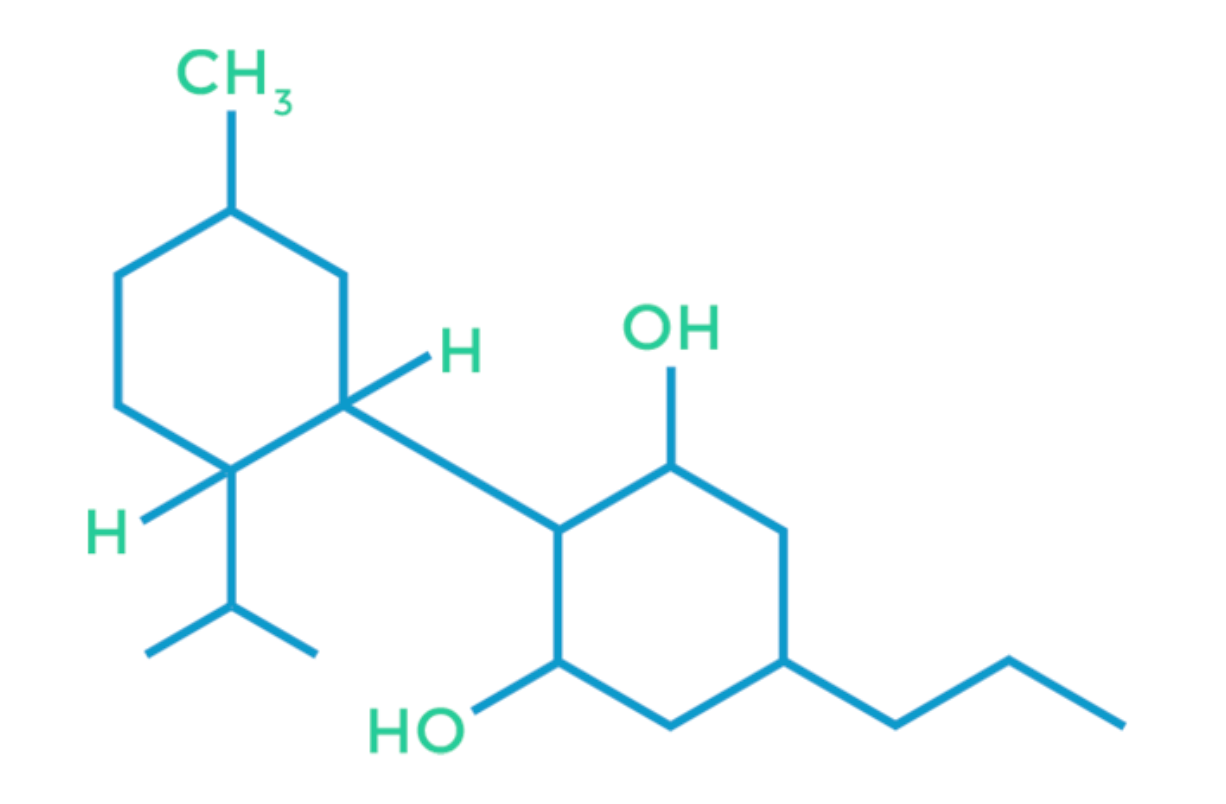
Cannabidiol, or CBD, is the non-psychoactive cannabinoid famed for significantly reducing symptoms in patients suffering from seizure and spasm disorders such as epilepsy and multiple sclerosis. CBD is the cannabinoid most often recommended for children, elderly and other patients who must remain clear-headed in their activities because it is non-psychoactive, meaning it will not produce euphoria or the feeling of being “high.”
CBD reacts with cannabinoid receptors throughout the human body and works to relieve inflammation and pain while producing a calming effect in patients. For this reason, it is often used to treat anxiety and sleep disorders. It has also been shown to work with THC to reduce the size of tumors.
Effects and Benefits
Research has shown that CBD is effective in the treatment of a variety of symptoms and conditions. Examples of conditions for which CBD is particularly effective in providing symptom relief are listed below:
- Cancer
- Seizures (including epilepsy)
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
- Chronic postoperative pain
LINKS TO RESEARCH
- Antitumor effects of cannabidiol, a nonpsychoactive cannabinoid, on human glioma cell lines.
READ STUDY →
- Cannabidiol as an emergent therapeutic strategy for lessening the impact of inflammation on oxidative stress.
READ STUDY →
- Cannabidiol displays antiepileptiform and antiseizure properties in vitro and in vivo.
READ STUDY →
- Antitumor activity of plant cannabinoids with emphasis on the effect of cannabidiol on human breast carcinoma.
READ STUDY →
